Solubility mystery solved
Induction effects explain differences in solubility of polyether molecules
30 June 2019
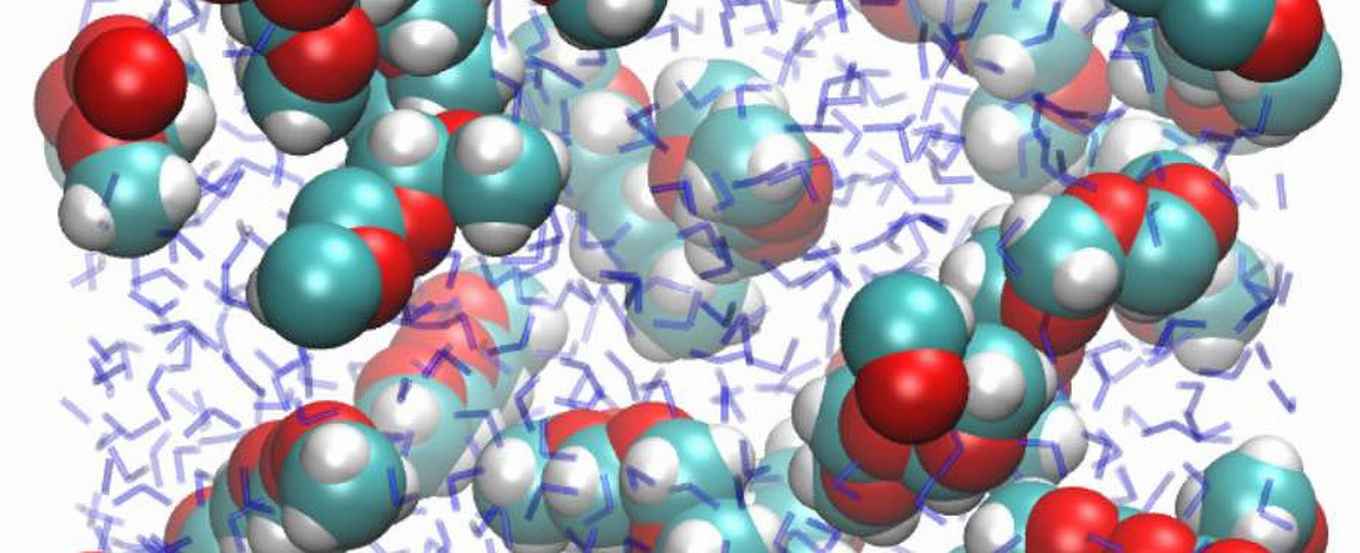
The researchers in particular shed light on the solubility differences between the polyethers PEG (polyethylene glycol) and POM (polyoxymethylene) that are everywhere in our daily lives. PEG has many applications in aqueous solutions for pharmaceutical and cosmetic purposes, for instance in creams for shaving and skin-care. POM is a ubiquitous plastic material: many objects in daily life are made of POM, as are the brightly-coloured Keck clips for connecting glassware, well-known to every chemist.
Although these two polyethers are much alike at the molecular level, they have very counterintuitive solubilities in water. PEG (repeating unit -CH2-CH2-O-) is perfectly soluble, and every chemistry student can tell you why: the oxygen atoms in PEG are slightly negatively charged, which makes them hydrophilic. This explanation seems to be confirmed by the comparable polymer PPG (polypropylene glycol, repeating unit -CH2-CH2-CH2-O-): it contains relatively fewer oxygen atoms than PEG, and is less soluble, which is perfectly logical.
But wait: POM (repeating unit -CH2-O-) contains relatively more oxygen atoms than PEG, so the explanation would suggest an enhanced solubility. However, POM is completely insoluble!
Induction as an explanatory principle
To unravel the mystery, the researchers from Amsterdam and Mainz used a combination of femtosecond-infrared spectroscopy, dielectric-relaxation experiments, quantum calculations and computer simulations.
The experiments showed that the water-polymer interaction, which determines the solubility, strongly depends on the carbon/oxygen ratio of the polymer. Interestingly, quantum calculations showed that this dependence is not due to the distance between the oxygen atoms in the polymer chain. This has often been proposed—the idea being that the oxygen-oxygen distance in PEG fits better into the hydrogen-bond network of water.
In Nature Communications the researchers now show that the relation between carbon/oxygen ratio and solubility involves induction: the oxygen atoms are negatively charged because they withdraw electron density from the neighbouring carbon atoms in the polymer chain. In PEG, each oxygen atom has two neighbouring carbon atoms fully to its disposal to withdraw electron density from. In POM, however, the oxygen atoms have to 'share' the carbon atoms between them, and therefore can withdraw less electron density. As a result, the partial negative charge on the oxygen atoms in POM is about twice as low as in PEG. The concept of induction would thus perfectly explain why POM is much less hydrophilic, and therefore insoluble.
Elegant confirmation
To confirm that the difference in oxygen partial charge indeed explains the solubility difference, the theoretical researchers in the team carried out an elegant computer experiment. First, they simulated a solution of POM molecules, which precipitated as expected. When they then changed the oxygen charges of POM to those calculated for PEG, the POM-with-PEG-charges promptly dissolved:
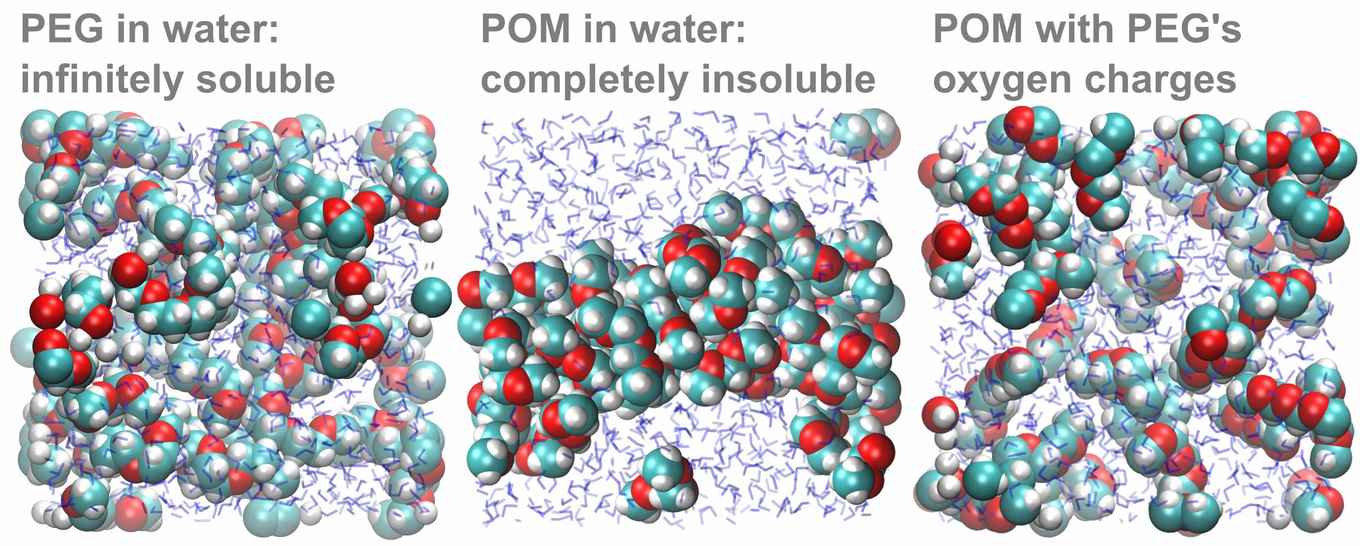
Besides solving a long-standing mystery related to everyday materials, the results show that induction effects can have a major impact on solubilities. Taking this effect into account should make it easier to predict solubilities in the future.
Publication details
Bernd Ensing, Ambuj Tiwari, Martijn Tros, Johannes Hunger, Sérgio R. Domingos, Cristóbal Pérez, Gertien Smits, Mischa Bonn, Daniel Bonn and Sander Woutersen. On the origin of the extremely different solubilities of polyethers in water. Nature Communications (2019) 10:2893 DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-10783-z