NWO XS grant for Paola Riente Paiva
To explore the use of magnetism in organic photocatalysis
21 December 2021

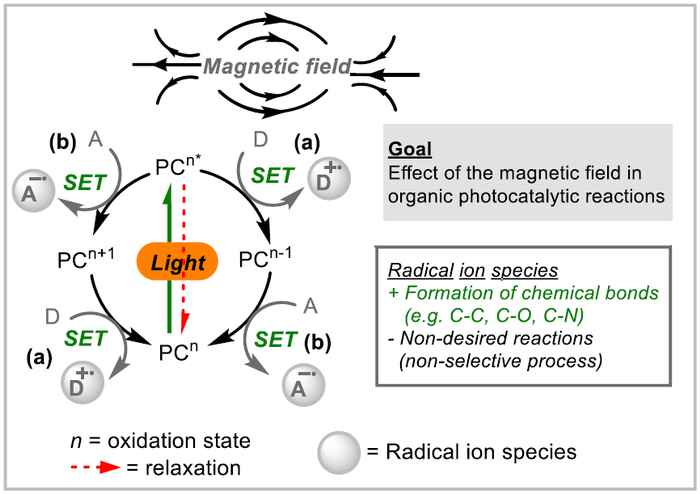
Photocatalysis is an enabling green technology that allows the transformation of light, either solar or artificial, into chemical energy. This is enabled by a photocatalyst, a chemical compound that can absorb light, triggering valuable chemical transformations. A key step in the reaction mechanism is the process of single-electron transfer where the photocatalyst interacts with organic compounds to generate radical species which are subsequently involved in the formation of chemical bonds.
To further develop the process of photocatalysis towards practical and economically relevant applications, it is crucial to improve the efficiency of the single-electron transfer and to control the reactivity of the radicals. To achieve this, Paola Riente Paiva will study the use of magnetic fields in homogeneous photocatalytic reactions. The magnetic fields can improve the efficiency of the single-electron transfer process and control the reactivity of the radical species involved, important steps toward the achievement of a fully efficient photocatalytic process.