How graphitic carbon nitride can render drug development more sustainable
3 June 2024
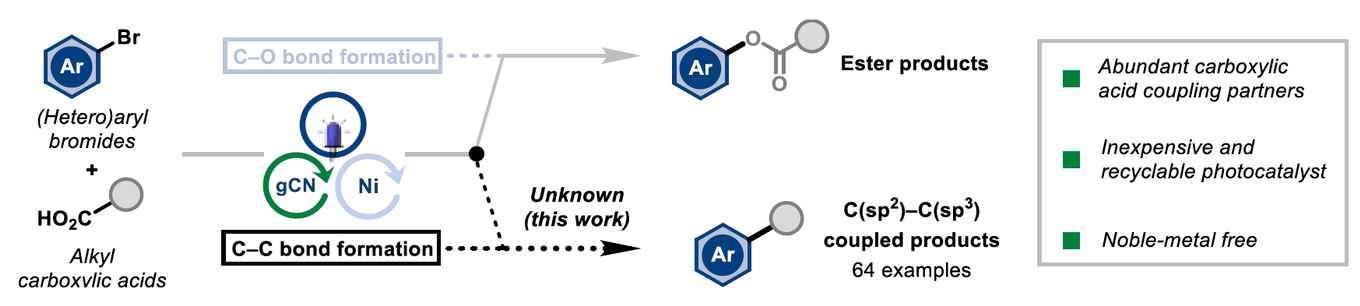
The paper describes how off-the-shelf heterogeneous semiconductor graphitic carbon nitride (gCN) can be used as a photocatalyst, combined with nickel catalysis, for the cross-coupling between aryl halide and carboxylic acid entities. In particular, the researchers demonstrate how the use of gCN favours the formation of C-C over C-O bonds. They also demonstrate the recycling of the photocatalyst and present an assessment of the environmental impact of graphitic carbon nitride, which represents a clear improvement when compared with rare-earth metals. The research was carried out in cooperation with Novartis.
Abstract of the paper
The development of robust and reliable methods for the construction of C(sp2)–C(sp3) bonds is vital for accessing an increased array of structurally diverse scaffolds in drug discovery and development campaigns. While significant advances towards this goal have been achieved using metallo-photoredox chemistry, many of these methods utilise photocatalysts based on precious-metals due to their efficient redox processes and tuneable properties. However, due to the cost, scarcity, and toxicity of these metals, the search for suitable replacements should be a priority. Here, we show the use of commercially available heterogeneous semiconductor graphitic carbon nitride (gCN) as a photocatalyst, combined with nickel catalysis, for the cross-coupling between aryl halide and carboxylic acid coupling partners. gCN has been shown to engage in single-electron-transfer (SET) and energy-transfer (EnT) processes for the formation of C–X bonds, and in this manuscript we overcome previous limitations to furnish C–C over C–O bonds using carboxylic acids. A broad scope of both aryl halides and carboxylic acids is presented, and recycling of the photocatalyst demonstrated. The mechanism of the reaction is also investigated.
Paper details
Florian Lukas, Michael T. Findlay, Méritxell Fillols, Johanna Templ, Elia Savino, Benjamin Martin, Simon Allmendinger, Markus Furegati, Timothy Noel: Graphitic Carbon Nitride as a Photocatalyst for Decarboxylative C(sp2)–C(sp3) Couplings via Nickel Catalysis. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, accepted article, first published 28 May 2024. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202405902
See also
Research group Flow Chemistry