Paper on chemical recycling of PET among top-cited publications of ACS Engineering Au
Offering a circular pathway for the reuse of plastic waste
3 November 2025
Research leader Dr Shiju Raveendran recently received notice from the editors of ACS Engineering Au that the paper was one of the top-cited papers of 2024 as well as one of the top downloaded papers from their website (over 15000 times). As of today, it still features in the journal’s list of most-read articles over the last 12 months and even over the last 30 days.
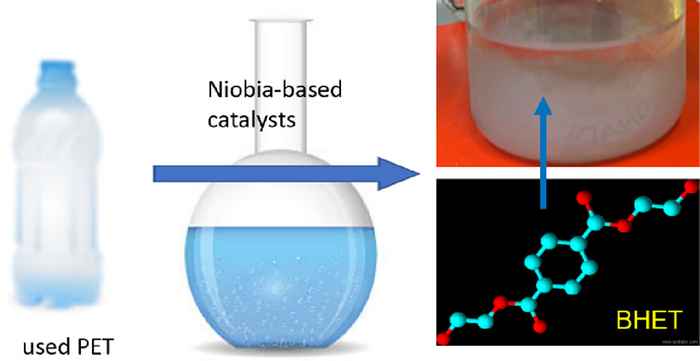
According to Raveendran, the popularity of the paper stems from its demonstration that chemical recycling can be both efficient and sustainable. “Our approach uses inexpensive and non-toxic niobia-based materials to efficiently convert waste PET into its original monomer, offering a circular pathway for the reuse of plastic waste. It also fits well within our group’s broader research on catalysis for sustainable chemical transformations.”
In their paper, the researchers present a method for depolymerisation of PET to its BHET monomer - bis(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate - via glycolysis, using ethylene glycol (EG) in the presence of niobia-based catalysts. A high yield toward the monomer was obtained at mild conditions. This approach allows recycling of the PET at reasonable conditions using an inexpensive and non-toxic material as a catalyst.
Paper details
Shadi Shirazimoghaddam, Ihsan Amin, Jimmy A Faria Albanese, and N. Raveendran Shiju: Chemical Recycling of Used PET by Glycolysis Using Niobia-Based Catalysts. ACS Engineering Au 2023 3 (1), 37-44. DOI: 10.1021/acsengineeringau.2c00029